What is Big Data?
Big data is a term used to present a data set of structured, unstructured, and semi-structured types. These data sets are difficult to store and process in current solutions provided by traditional database systems. The major challenges for such huge data are storing, analyzing, transferring, searching, and so on.

Characteristics of Big Data:
There are five characteristics of Big Data which are mentioned below.
- VOLUME
- VELOCITY
- VERACITY
- VARIETY
- VALUE

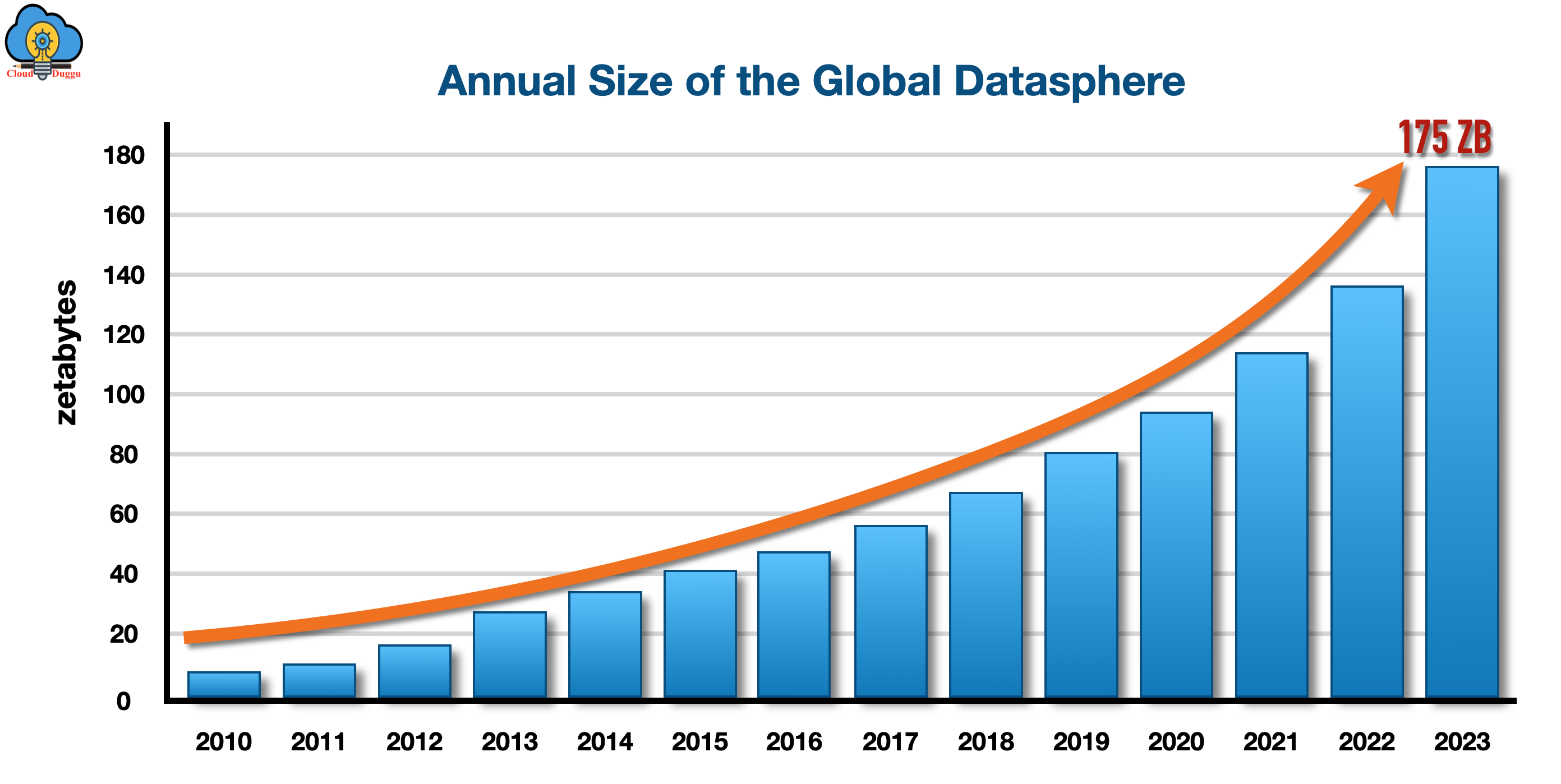
1. What is VOLUME?
Volume is defining the “Huge Amount of Data” which are generating every day at a high rate and sources of such huge data are Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, IoT, etc. Please refer to the below trend to understand it more.
2. What is VELOCITY?
Velocity refers to the pace at which different sources are generating data on daily basis. The data flow is getting high and in continuous form. There are 1.50 billion daily active users (Facebook DAU) on mobile as of now, which is an increase of 25% year-over-year. These stats project the pace at which users are increasing and the data that each user is generating. If velocity can handle then data insight can be generated and the decision can be taken based on real-time data.

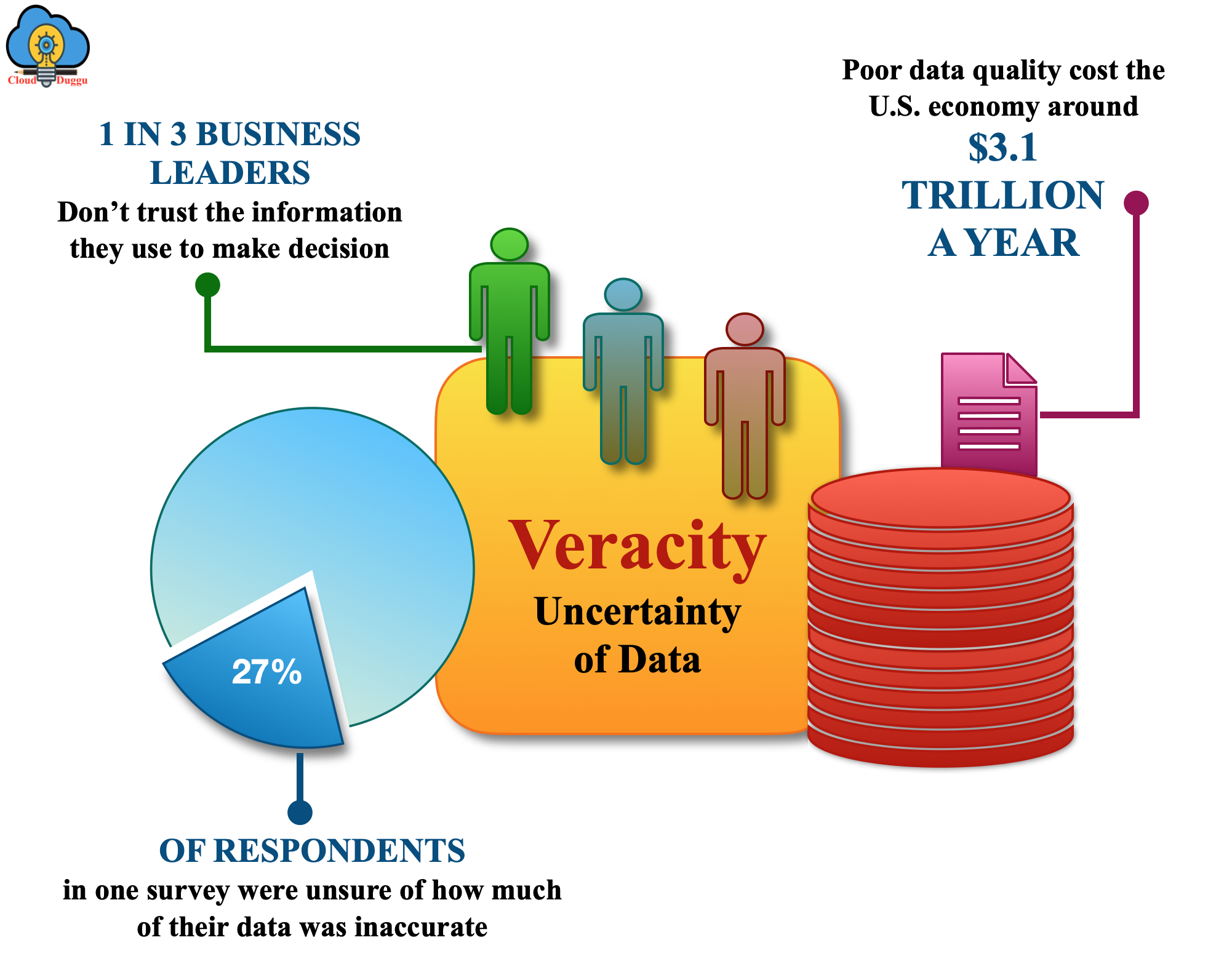
3. What is VERACITY?
Veracity represents the uncertainty of data that are available due to incompleteness and inconsistency of data. In some cases, available data is so disordered that it can’t be trusted. Due to the volume of such data, it is very difficult to maintain quality and accuracy.
Most business leaders don’t use such data to make any business decision because the behavior of data is not certain.
In a survey, it was discovered that 27% of respondents were unsure of how much of their data was inaccurate.
US economy faces a $3.1 trillion cost every year for such poor quality data.
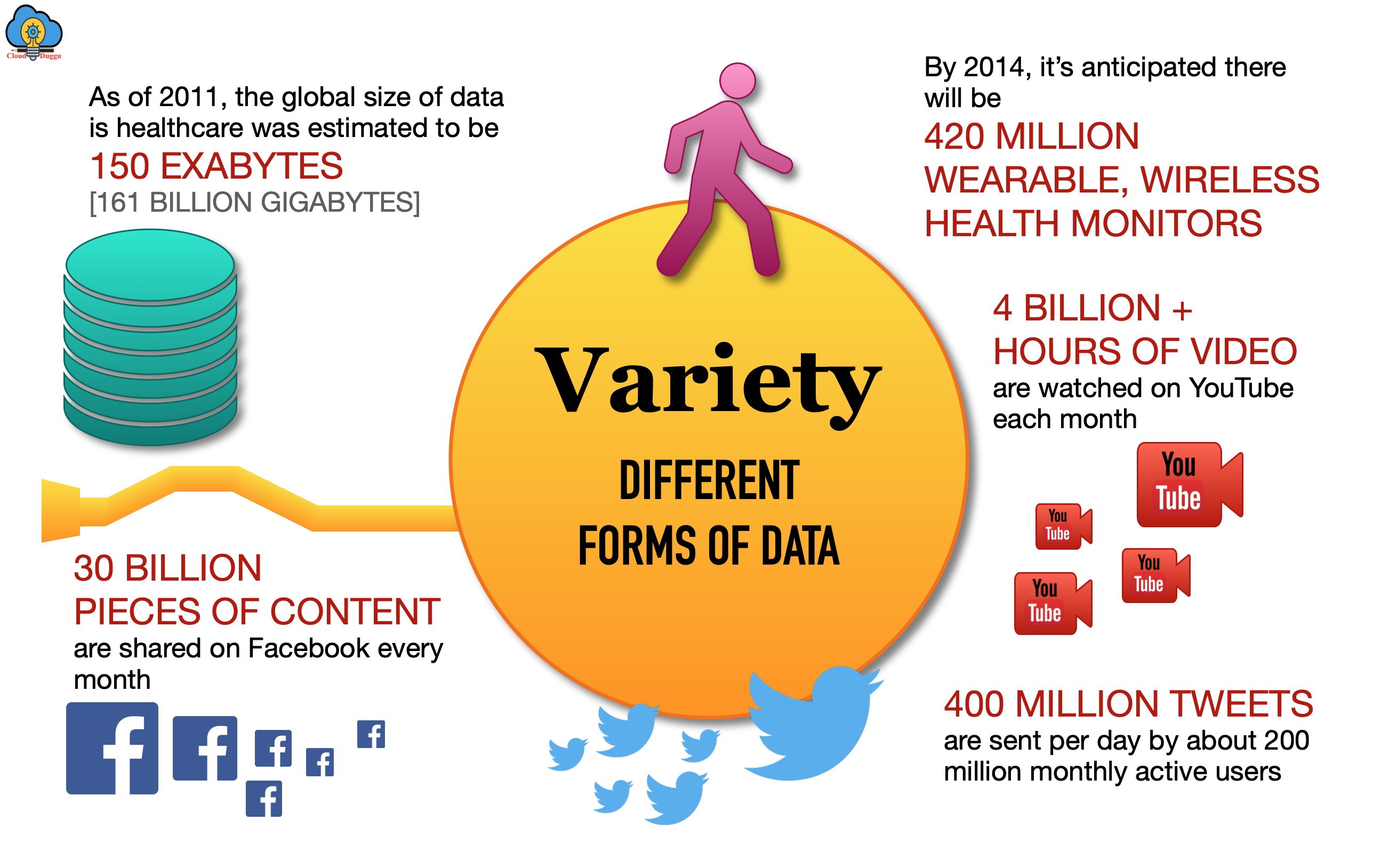
4. What is VARIETY?
Variety refers to the type of Data such as Structure, unstructured, and semi-structure as many sources are generating different types of data. In past data, generation was not that high, and the form in which data was generating excel, text, and database but now a day’s data is getting generated from many sources and types of data also change such as sensor, audios, images, videos and so on.
5. What is the VALUE?
Value refers to the usefulness of data in decision-making; it is adding value to the organization by analyzing a large amount of big data, without adding any value, data is of no use.

Big Data Types
Let us understand Big Data types, there could be three types of data present which are mentioned below.
- Structured
- Semi-Structured
- Unstructured
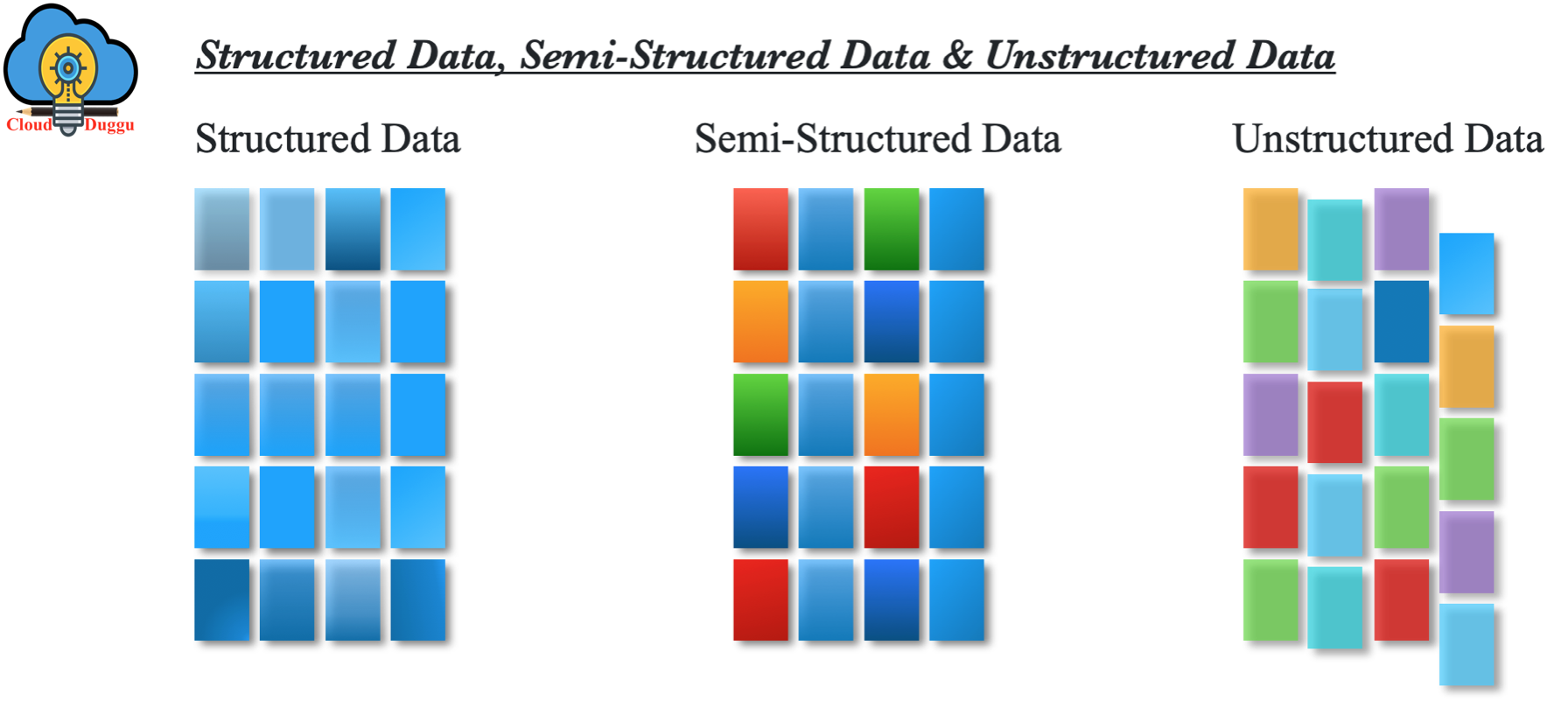
1. Structured Data
The data type which can be stored and proceed in a fixed format (table format) is called structured data. In traditional database management systems (Oracle, MS SQL… etc.) data is stored in fixed format and data can be easily processed with SQL (Structured Query Language) language. In structured data format first, we need to define the data model that will illustrate how data is organized, accessible and processed such as we can define columns, their data types, and so on.
Example of Structured Data: Dates, Phone Numbers, Credit Card Numbers, Addresses, etc.
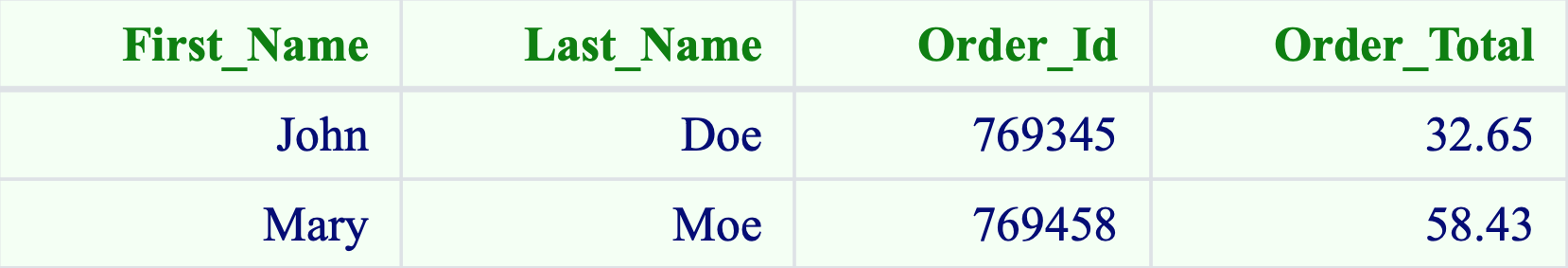
2. Semi-Structured Data
A semi-structured data type is a data type that does not have a fixed format and can’t reside in fixed fields or format but it has some organizational properties such as tags and other indicators to separate elements.
Example of Semi-Structured Data: JSON files, XML, .CSV files, tab delimited files etc.

3. Unstructured Data
The data type which has an unknown format and which cannot be stored in RDBMS and cannot be analyzed until unless it will be converted into a structured format is called unstructured data. Unstructured data is growing quickly as experts say 80% of data in an organization are unstructured.
Example of Unstructured Data: Text Files, Reports, Web Logs, Audio Files, etc.

Big Data Applications
Let us have a look at Big Data applications.
- Retail/Consumer
- Finances & Frauds Services
- Web and Digital Media
- Health & Life Science
- Telecommunications
- Ecommerce & Customer Service
Big Data Examples
The following are the example of big data which are growing day by day.
- Walmart is processing millions of customer transactions per hour.
- Facebook stores, accesses, and analyses 30+ Petabytes of user-generated data.
- On daily basis, there are more than 230+ million tweets are getting created.
- Worldwide, more than five million people are using the mobile phone to make calls, sending text, tweeting.
- On YouTube, every minute, there are 48 hours of videos are getting uploaded.
- Amazon is handling fifteen million customer clicks per day to make a recommendation of products.
- Every day, there are 294 billion emails are being sent.
- Automobile sectors are using more than a hundred sensors to monitor the behavior of Cars such as fuel level, the pressure of tires, and so on.
Big Data Challenge
There are a few challenges with big data, which are mentioned below.
1. Data Analysis
Producing value from such huge and disordered data is very challenging because data is very hard to understand and working on such data and creating meaningful results is even more difficult.
2. Storage System
Handling such huge data involve high storage as well because conventional storage racks are very costly. So to resolve this problem there should a storage system that can scale up and down based on the requirement.
3. Nature of Data
Data coming from different sources are very messy, inconsistent, and incomplete. Originations are spending a very high amount of money to get the value from data.
4. Lack of Trained Professionals
Big Data resources are very laborious to find who has complete knowledge of Big data ecosystem.
Big Data Solution
HADOOP is the solution to all these challenges.
Advantage of Hadoop.
- Hadoop is a java based programming framework that supports storage and data processing of large data sets in distributed environments.
- Hadoop handles a large volume of structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data more effectively than legacy data warehouse systems.
- Hadoop can run on commodity (Cheap Storage) hardware.
- Hadoop has a robust community that is working towards its enhancements.

