DML commands are used to perform data manipulation operations such as putting data into a table, retrieving data from a table and deleting schema, and so on.
Apache HBase supports the below list of DML commands.
Let us see each DML command in detail.
1. Put
Put command is used to insert data in a table
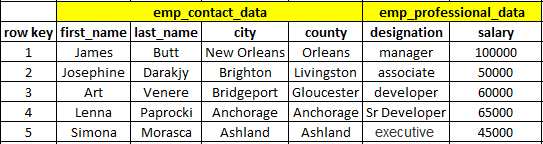
To perform the Put operation, we will create a table with the name "employee" and insert data.
The structure of the table should look like below.
Syntax
hbase(main):015:0> put <'tablename'>,<'rowname'>,<'columnvalue'>,<'value'>
Command
hbase(main):015:0> create 'employee','emp_contact_data','emp_professional_data'
hbase(main):016:0> put 'employee','1','emp_contact_data:first_name','James'
hbase(main):017:0> put 'employee','1','emp_contact_data:last_name','Butt'
hbase(main):018:0> put 'employee','1','emp_contact_data:city','New Orleans'
hbase(main):019:0> put 'employee','1','emp_contact_data:county','Orleans'
hbase(main):020:0> put 'employee','1','emp_professional_data:designation','manager'
hbase(main):021:0> put 'employee','1','emp_professional_data:salary','100000'
hbase(main):022:0> put 'employee','2','emp_contact_data:first_name','Josephine'
hbase(main):023:0> put 'employee','2','emp_contact_data:last_name','Darakjy'
hbase(main):024:0> put 'employee','2','emp_contact_data:city','Brighton'
hbase(main):025:0> put 'employee','2','emp_contact_data:county','Livingston'
hbase(main):026:0> put 'employee','2','emp_professional_data:designation','associate'
hbase(main):027:0> put 'employee','2','emp_professional_data:salary','50000'
hbase(main):029:0> put 'employee','3','emp_contact_data:first_name','Art'
hbase(main):030:0> put 'employee','3','emp_contact_data:last_name','Venere'
hbase(main):031:0> put 'employee','3','emp_contact_data:city','Bridgeport'
hbase(main):032:0> put 'employee','3','emp_contact_data:county','Gloucester'
hbase(main):033:0> put 'employee','3','emp_professional_data:designation','developer'
hbase(main):034:0> put 'employee','3','emp_professional_data:salary','60000'
hbase(main):035:0> put 'employee','4','emp_contact_data:first_name','Lenna'
hbase(main):036:0> put 'employee','4','emp_contact_data:last_name','Paprocki'
hbase(main):037:0> put 'employee','4','emp_contact_data:city','Anchorage'
hbase(main):038:0> put 'employee','4','emp_contact_data:county','Anchorage'
hbase(main):039:0> put 'employee','4','emp_professional_data:designation','Sr Developer'
hbase(main):040:0> put 'employee','4','emp_professional_data:salary','65000'
hbase(main):041:0> put 'employee','5','emp_contact_data:first_name','Simona'
hbase(main):042:0> put 'employee','5','emp_contact_data:last_name','Morasca'
hbase(main):043:0> put 'employee','5','emp_contact_data:city','Ashland'
hbase(main):044:0> put 'employee','5','emp_contact_data:county','Ashland'
hbase(main):045:0> put 'employee','5','emp_professional_data:designation','executive'
hbase(main):046:0> put 'employee','5','emp_professional_data:salary','45000'
Output



2. Count
Output



2. Count
The count command is used to count the number of rows present in a table. Using the “Cache” option we can restrict the row which should be displayed. The default size of “Cache” is 10 rows.
Syntax
hbase(main):047:0> count <'tablename'>, CACHE =>1000
Command
hbase(main):047:0> count 'employee'
The below command is fetching 1000 rows at a time. In the output, the result is showing only five rows because there are only five rows present in table “employee”.
Output

3. Get
Get command is used to read data from a table.
Using the get command, we can read a single row of data at a time.
Syntax
hbase(main):051:0> get ’<table name>’,’row1’
Command
hbase(main):051:0> get 'employee', '1'
Output

Output

We can read a specific column as well using the ‘get’ command.
Syntax
hbase(main):052:0> get 'table name', ‘rowid’, {COLUMN ⇒ ‘column family:column name ’}
Command
hbase(main):058:0> get 'employee','1',{COLUMN => 'emp_contact_data:first_name'}
Output

4. Scan
Output

4. Scan
Scan command is used to view the complete data of a table “employee”.
Syntax
hbase(main):059:0> scan ‘<table name>’
Command
hbase(main):059:0> scan 'employee'
Output

5. Delete
Output

5. Delete
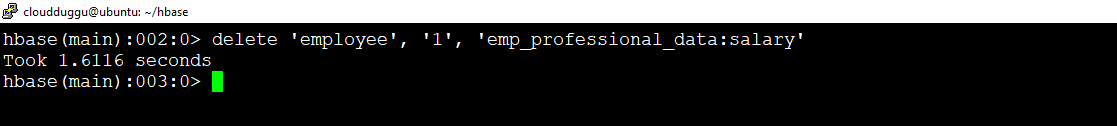
Delete command is used to delete a specific cell in a table.
Syntax
hbase(main):001:0>delete ‘<table name>’, ‘<row>’, ‘<column name >’, ‘<time stamp>’
In this example, we are deleting a specific cell.
Command
hbase(main):002:0>delete 'employee', '1', 'emp_professional_data:salary'
Output
6. Deleteall

6. Deleteall
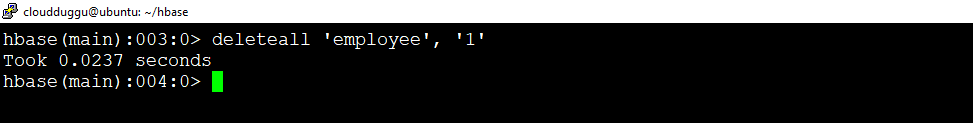
Delete all command is used to delete all cells in a row.
Syntax
hbase(main):003:0> deleteall ‘<table name>’, ‘<row>’
In this example, we are deleting all cells in a row.
Command
hbase(main):003:0> deleteall 'employee', '1'
Output
7. Truncate

7. Truncate
The truncate command is used to delete all rows and columns in a table. It will delete only data and not the structure of the table.

