Apache Solr provides the feature to query the documents using the Query option, which is stored in the index. We can use the Query option to perform a different type of search operation and analysis on the documents which are stored in the Solr index and fetch the results.
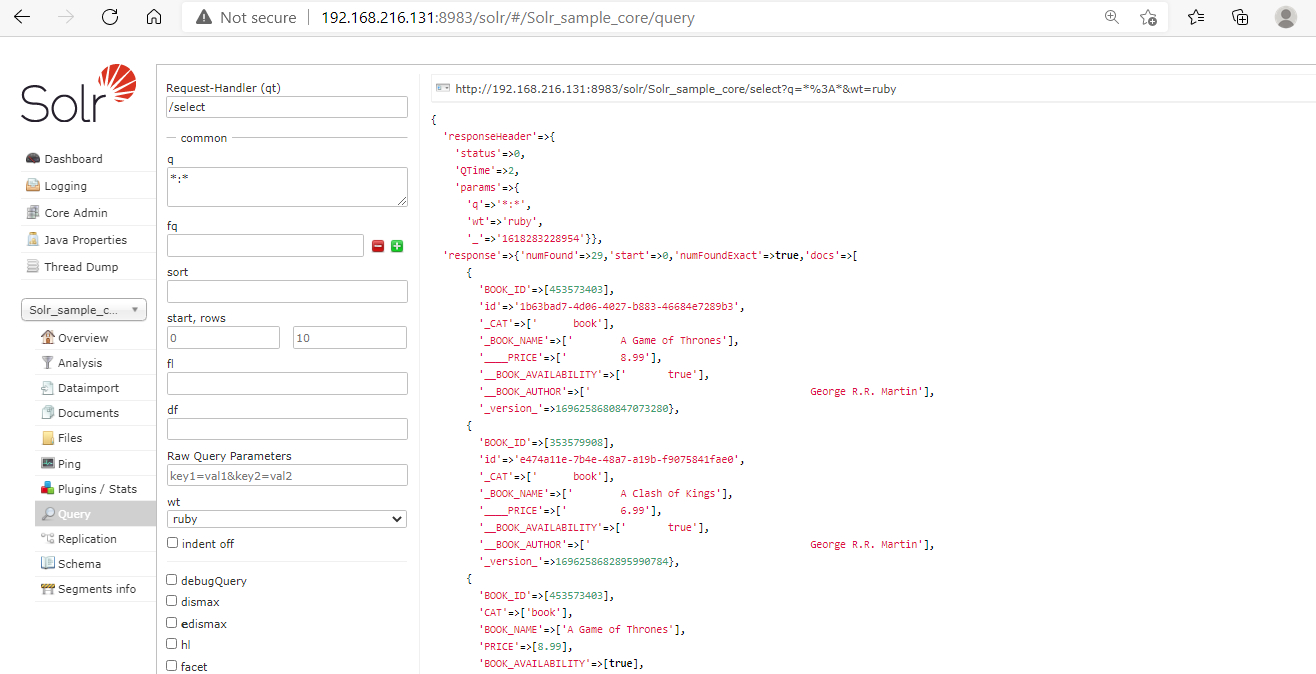
The following figure represents the Query option of the Apache Solr Web interface that we can start at http://localhost:8983/.
Apache Solr Query Options
The following is the list of different parameters available in Apache Solr Query with their description.
| Query Parameter | Detail |
|---|---|
| q | In this parameter, we put the query that needs to be searched in Apache Solr index. |
| fq | Using this parameter we can restrict the document result set. It works as a filter condition. |
| start | This is the starting point of a page result, The default value is 0. |
| rows | This parameter shows the number of pages that will be retrieved based on the search condition. The default value is 10. |
| sort | Using this parameter we can perform the sort operation based on the fields. |
| fl | Using this parameter we can specify the field name that will be returned. |
| wt | Using this parameter we can see the response writer type. |
| indent | Using this option we can receive more readable responses. |
| debugQuery | Using this option we can receive debugging information such as "explain info" of documents. |
| dismax | Using this option we can enable the Dismax query parser. |
| edismax | Using this option we can enable the Extended query parser. |
| hl | Using this option we can highlight the query response. |
| facet | The facet allows performing search operations based on the classification of the search query. |
| spatial | Using this option the geospatial searches data can be captured. |
| spellcheck | This option provides an inline query Spellchecker. |
Retrieving the Records From Apache Solr Index
We can fetch the records which are stored in Apache Solr by passing different parameters in the Solr Query page. In the previous section, we created the core name Solr_sample_core and stored JSON and XML documents. In this section let us see the various option to see those index records.
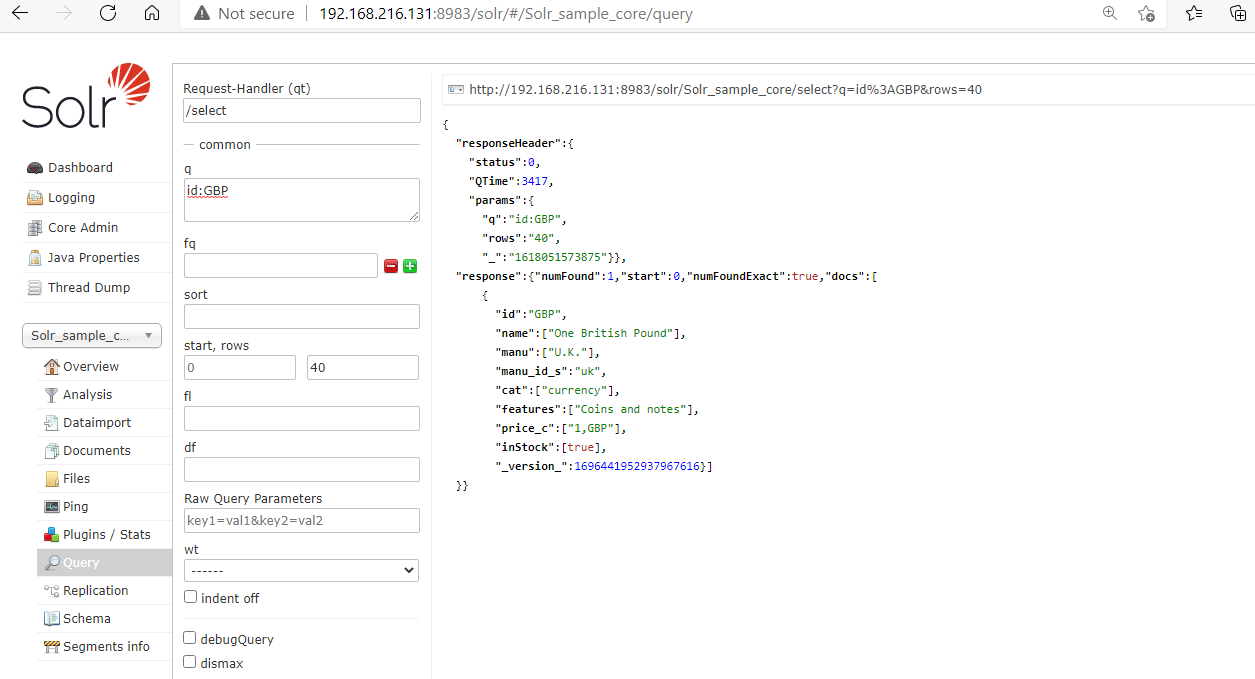
1. Fetching Records using Field ID.
We can use the document field ID to fetch the records for that we need to pass the particular field name in the q< section of the Query page. For example, we stored the moneydata.xml XML file in the Document addition section now we will pass the ID=GBP to fetch the record.
After processing the below records will be shown.
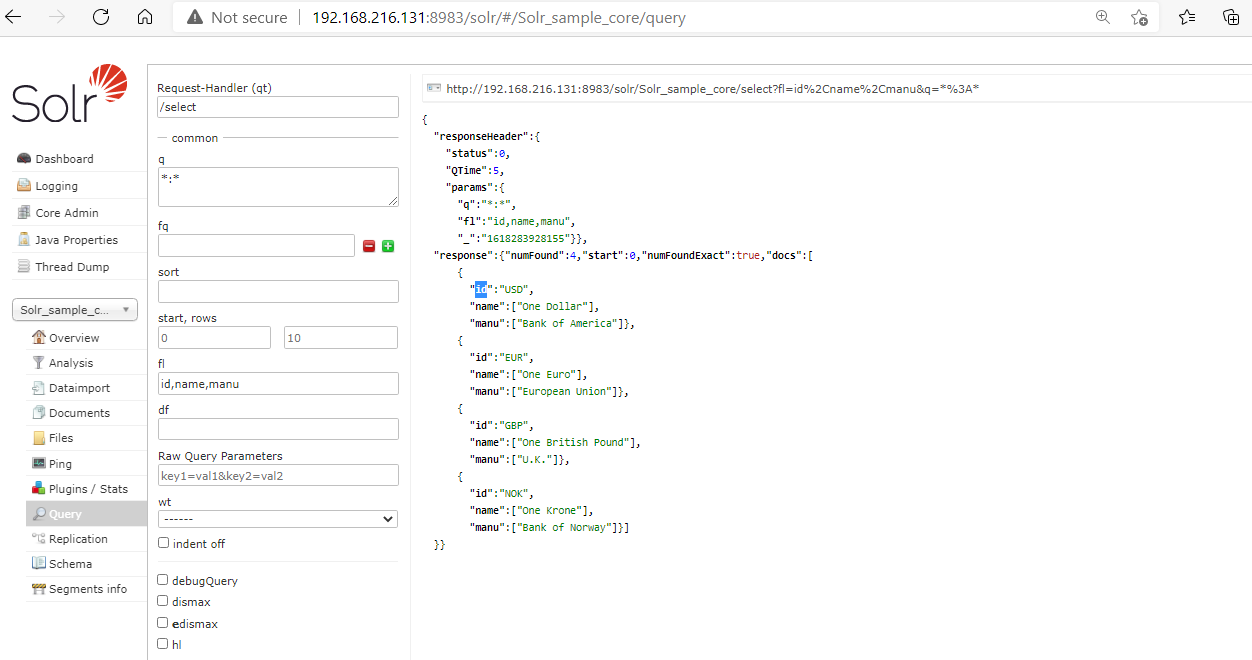
2. Fetching Records using Field Name.
We can fetch the documents bypassing the field name in the fl option of the Solr Query page. For example, we want to see the field name which is "id, name, manu" then we will pass this in the fl textbox and run the query.
We can see from the below output that only matching records are displayed.
3. Fetching All Records
We can fetch all documents which are stored in Apache Solr Index bypassing the *:* parameter in the q section of the Solr Query page.
After processing the following output is shown.
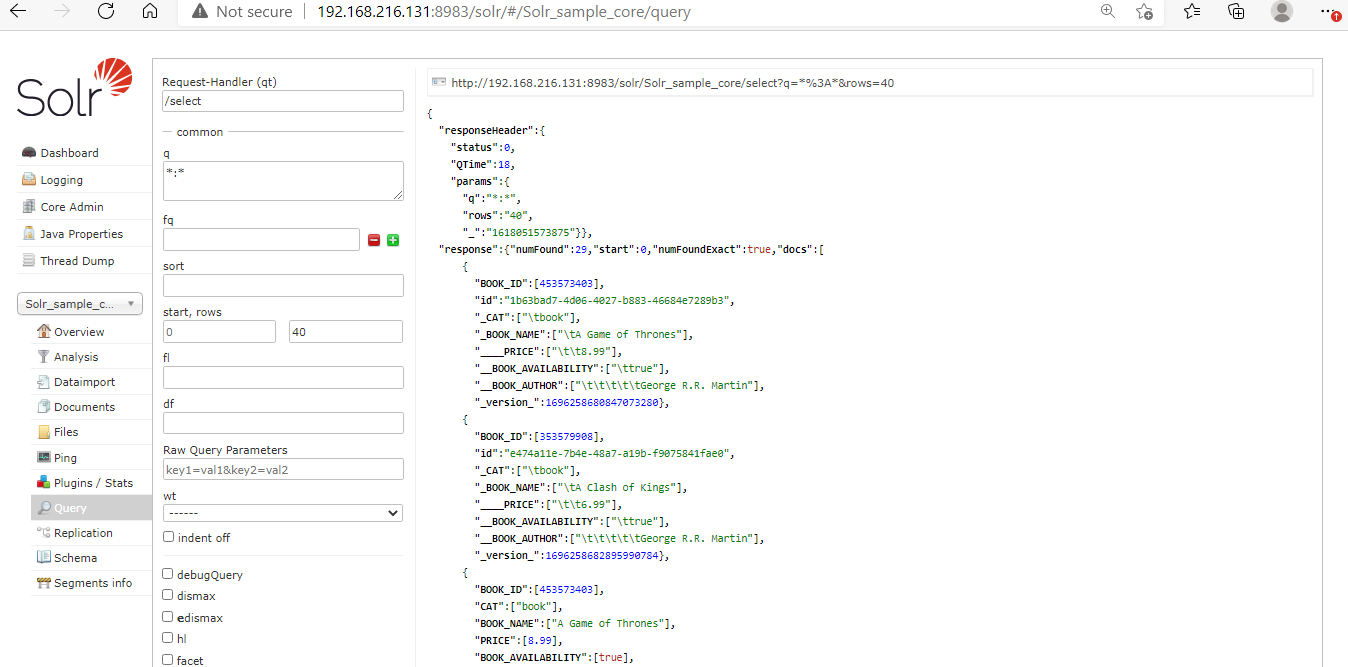
4. Fetching All Records from 2nd Value
To fetch the records from the 2nd place from the Solr index, we can pass the value from 2nd place, pass the 2 in the start box, and the number of rows you want to see in the rows box. After processing the following records will come.
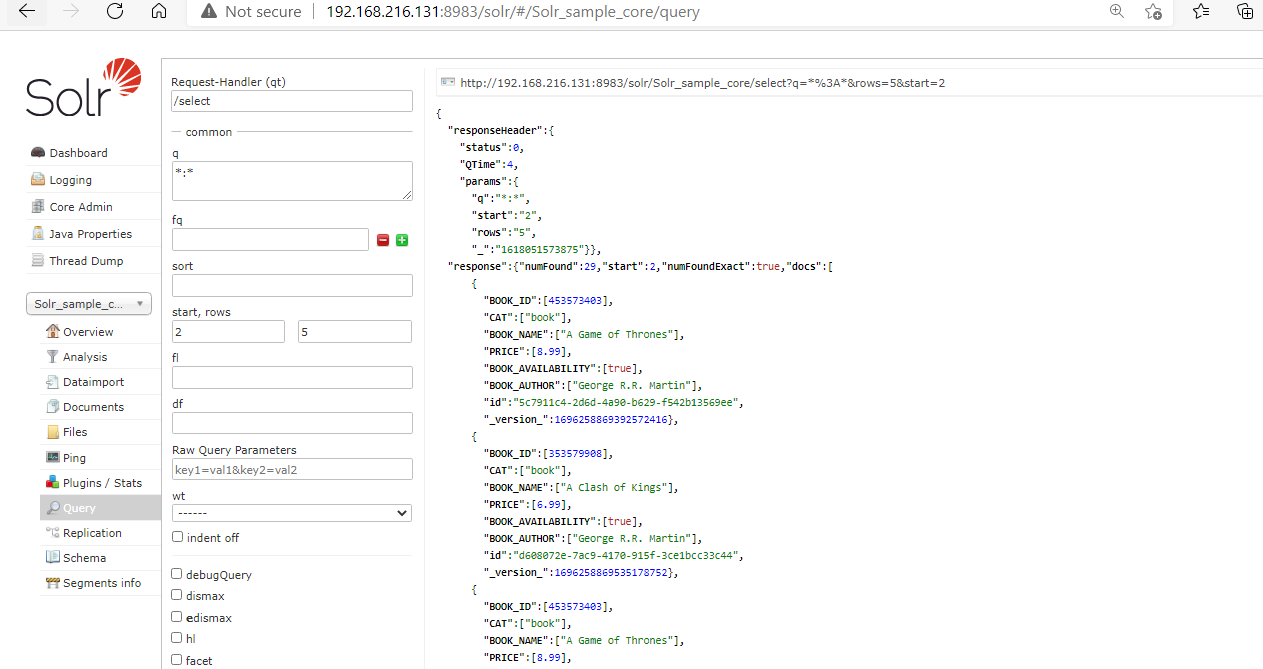
5. Solr Response Writer Type
Using the Apache Solr Response writer, we can fetch the document in JSON, XML, Python, Ruby, CSV, and PHP format. For example, in the below figure we have selected the Ruby document format and we can see on the right side the documents are shown in the Ruby format.